Integrating Technology into Teaching: Technological Pedagogical Content Model (TPACK), and Its Implications
Mary Jane Özkurkudis, Turkey
Mary Jane Özkurkudis is an instructor at Izmir University of Economics, Turkey. She holds a BA degree in English Language and Literature and is currently doing her MA on Curriculum Development and Instruction. She is interested in professional development and thus, has completed numerous courses on ELT. Her main field of interest is curriculum and instructional design.
E-mail: mary.ozkurkudis@ieu.edu.tr
Menu
Introduction
Integrating technology into teaching
Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK) Model
Content Knowledge
Pedagogical Knowledge
Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Technological Knowledge
Technological Content Knowledge
Technological Pedagogical Knowledge
Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge
Conclusion
References
Education is a constantly enhancing and changing process based on the needs of the society and the era. Therefore, for increased sustainability in education both the institutions and the educators need to adapt themselves to the changes based on these needs. Nowadays, we can see that teachers deal with complex and dynamic classrooms leading to mainly a need for improvement and professional development in the field of technology. For an effective learning environment, teachers should follow a programme where different areas of knowledge can be integrated. This consists of knowing the subject to be taught, being aware of the way learners learn and think, and recognizing the ways to improve technological knowledge.
The use of information technology tools is widespread among educational institutions; however, it is clearly seen that there are some factors that hinder this use. These may be defined as external and internal factors. It should be kept in mind that external factors such as; covering financial needs, building the relevant infrastructure systems, preparing a technologically-friendly environment should be accomplished before introducing the use of technology in education to both educators and learners. Taking into consideration the internal factors, we can say that teachers still have difficulties in integrating these tools into their lessons or some still do not know how to use them and; therefore, ignore using them. One way to overcome this obstacle is to provide appropriate training after which teachers will feel confident and safe to integrate this technology into their lessons. A variety of integration models have also been introduced to overcome the reluctance to use technology and the problems faced concerning integration. It is never possible to say one model is better than the other as they all serve different needs. One model is called Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK). The main components of this framework and the relation between them play an important role in establishing an effective teaching and learning environment.
This model was developed taking into account Schulman’s (1986-1987) Pedagogical Content Knowledge. Based on the needs of the era, a new component, technology, was added to this model and was firstly introduced in literature of education in 2003 (Chai, et.al, 2013). It is comprised of three components; technology, pedagogy and content, and emphasizes the interaction between them. Thus, the framework aims for the effective use of these three concepts of knowledge.
This knowledge entails the knowledge of the teachers concerning the subject to be taught and learned. This type of knowledge consists of theories, approaches, concepts, evidence and proof (Koehler, et.al., 2013). The role of the teacher is vital in the sense that s/he should possess information and knowledge about the subject to be taught as a lack of it may lead to mishaps in learning; thus, resulting in the wrong acquisition of the subject matter. To give an example, having knowledge about a specific subject like history and geography means meeting the prerequisites of this component. This knowledge focuses on the question “What is the aim of the curriculum and will the ideas of the teacher be of use to the learners?” (TPACK Model, 2010).
This type of knowledge can be described as the knowledge and competence of the teacher in terms of methodology. The ways learners learn, classroom management skills and assessment methods are parts of this component. In other words, the strategies and methods used in class, the characteristics of the target audience and the assessment strategies are the concerns of this field (Chai, et.al, 2013). A teacher with pedagogical knowledge knows how learners acquire information, how they use it and how they improve it as s/he is equipped with the necessary skills to perform his/her profession. This content focuses on the knowledge of how to teach rather than what to teach. It answers the question “What kind of strategies can be used?” (TPACK Model, 2010).
This knowledge requires the teacher to teach the content of his/her field based on the learning styles of the learners, by using a variety of methods, and by adapting or changing course material. The teacher should have both the knowledge and skill, should know what to teach and how to teach it. Teaching comparatives using similes can be an example for this content. Another example can be turning a reading text into a running dictation activity to cater for learners with different learning styles. “What pedagogy is the curriculum based on?” (TPACK Model, 2010) can be a question to answer when focusing on this content.
Technological knowledge combines the required and adequate technological knowledge and the effective use of information technology tools in daily life (Chai, et.al, 2013). A person with this knowledge can complete tasks using technology and aims to constantly improve it. This field requires being technology literate and following the recent trends. The teacher is not expected to be an expert in technology but to know the basic skills to be able to use software and to cope with minor problems. Knowing how to use social websites or sending and receiving e-mails can be examples of this type of knowledge. In this context the question “What kind of technological knowledge do we need to meet the curriculum goals and pedagogical approach?” can be answered (TPACK Model, 2010).
This type of knowledge is a good indicator of how content is related to technology, how these two fields affect each other and in what sense they restrain each other. What is expected from the teacher is more than just to teach the content, but choosing the best technology and using a variety of information technology tools (Koehler, et.al, 2013). Moreover, the teacher should be able to take the initiative to adapt the course material where possible so as to meet the needs of learners. When doing so s/he should keep in mind not to use technology just for the sake of using it; however, applying it where necessary. Knowing how to prepare presentation slides, being familiar with educational websites are examples of this content. The main concern of this type of knowledge is how technology affects the curriculum and how activities can be adapted to meet the needs of the technology literate generation (TPACK Model, 2010).
Technological pedagogical knowledge shows how teachers can change when using specific technologies. This field is crucial as most software is designed for communicative purposes or to meet professional requirements. Here, the teacher’s goal is to integrate these technologies into teaching (Koehler, et.al, 2013). For example, using “whatsapp or Skype” for educational purposes. The aim shifts from using technology in the classsroom to integrating it into the course material. Allowing learners to take part in the process is significant, in that way learners will be more active. Learners can create their own presentations, record videos or complete online tasks. The focus is on how technology affects the teacher’s pedagogy and how to use technology so that learners can achieve the aims of the lesson (TPACK Model, 2010).
The TPACK Model covers all the main components (content, pedagogy, technology) for learning and teaching but it is different from knowing each component on its own. It requires teaching by having knowledge about a specific field, taking into consideration learner types, using the correct pedagogical methods and approaches, and using the appropriate information technology tools. It is a synthesis of all the fields (Koehler, et.al., 2013). It is a framework that requires the use of all these components to accomplish the goals of a lesson. To better explain the model with an example, it can be said that using the TPACK Model means knowing what the prepositions of place are, how to teach them using different strategies and techniques and teaching them by integrating technology. As previously mentioned, knowing each component on its own will not create an effective learning environment. It is not being good in only one field but it is being able to combine all the three fields to achieve required success.
However, while implementing this model, the teaching environment and the infrastructure provided should be taken into account as the model will differ in a classroom where all students have access to the internet whereas only the teacher has access in another. Therefore, referring back to the external factors affecting the integration of technology into teaching, it can be said that the institution needs to be ready to implement such a model.
Integration of technology into teaching has recently been introduced and has started to be widely used in contemporary education. A variety of learning management systems are being used, the classrooms are equipped with any sort of technology, digital books are introduced and the internet is full of online activities. Therefore, I can conclude by saying that the impacts of technology on education will continue to be seen as new technologies are introduced. Thanks to the TPACK model teaching and learning have become more efficient and technology now, is considered to have become a tool in achieving aims and learning objectives rather than just being used outside the classroom.
Chai, C.s., Koh, J., Tsai, C. (2013) A Review of Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge. Educational Technology & Society, 16 (2), 31-51. Retrieved from
www.ifets.info/journals/16_2/4.pdf on 02.01.2017.
Koehler, M.J., Mishra, P., Cain, W. (2013) What is Technological Content Knowledge (TPACK)?. Journal of Education, 193(3). Retrieved from
https://www.bu.edu/journalofeducation/files/2014/02/BUJoE.193.3.Koehleretal.pdf
on 02.01.2017.
TPACK Model (2010). Retrieved from
www.learningfutures.com.au/tpack-model on 02.01.2017.

Please check the Practical Uses of Technology in the Classroom course at Pilgrims website.
Please check the Practical Uses of Mobile Technology in the Classroom course at Pilgrims website.
Please check the How to be a Teacher Trainer course at Pilgrims website.
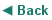

|